What is RFID technology? Applications, Working Principal, Types, Projects
Table of Contents
What is RFID technology?
RFID is a technology by which objects can be tracked and identified using electromagnetic fields. RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification. An RFID system consists of an RFID reader known as a Proximity Coupling device (PCD) and RFID tags known as Proximity Integrated Circuit Cards (PICC).
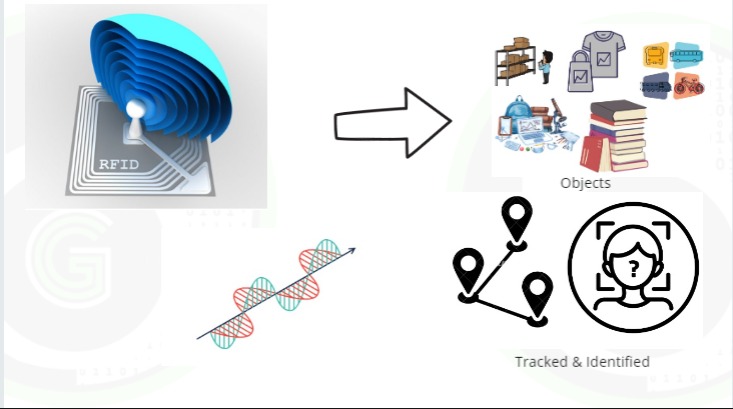
RFID Tags are attached to the objects which need to be tracked/identified and each tag has a unique value hard coded. RFID readers are attached to the main system/computer where all the processing takes place. Now, these tags are brought in close proximity to the RFID readers, RFID readers decode the value and send the information to the main system for tracking/identifying/monitoring purposes depending on the application.
RFID technology is similar to a barcode or the magnetic stripe of a credit card, as the data encoded in the label or magnetic strip can be captured by a device and stored in a database.
RFID belongs to a group of technologies referred to as automatic identification and data capture (AIDC). AIDC methods automatically identify objects, collect data about them and enter the data directly into systems with little or no human intervention. RFID methods use radio waves and automation technologies to accomplish all of this.
This technology has grown a lot since its first application. It has not only been improved over the years but also the cost of implementing and utilizing it continues to minimize, making this technology more efficient and affordable.
In its simplest form, an RFID system consists of 2 components: an RFID tag and an RFID reader. Refer to the section below to know more in-depth about RFID tags and Readers.

RFID tags are used to track objects, by reading/writing information on them and are usually composed of an integrated circuit, antenna, and battery. The integrated circuit stores the data and powers the antenna, allowing it to be read by a reader. Tags contain digitally encoded information that is stored in the integrated circuit and is transmitted to the reader.
Readers are devices that intercept, decode, and interpret the information stored in the tag. Typically, readers consist of RFID antennas, multiple operating modes (active and passive), frequency capabilities, and signal processing. The readers, antennas, and tags work together to collect data from RFID tags and transmit it to computer systems.
RFID Reader (PCD)
PCD(Proximity Coupling device): Also known as RFID readers. They decode the RFID Tags and communicate with them based on ISO14443 standard. PCD can perform read and write operation of data i.e bidirectional communication once PCD and PICC are coupled together. The coupling between PCD and PICC is based on inductive coupling (Refer to Working principle of RFID technology to know physics behind it).PCD energizes the PICC by coupling with them when PICC comes in close vicinity of PCD.And PICC gets energized, it starts transmitting its radio signals with UID of it. For energizing the PICC, they need to be brought in close proximity so that PCD magnetic fields get properly coupled with PICC.
PCD’s have the memory(FIFO buffers, EEPROM), communication pins for Host Interface(I2C,SPI,UART), antenna for generating of radio signals, power supply, I/O pins(Interrupt and Timer pins), small CPU for processing of data(CRC,Interrupt controller, Timer unit), Analog interface for RF front head(oscillators, PLL, PGA and etc), Low power modes and support of multi protocols for decoding tags.
PCD has the crypto features also implemented inside them, so that only authenticated RFID readers can communicate with PICC. And this also becomes the distinguishing feature in different PCD’s. Like NXP semiconductors, RFID readers follow the crypto-1 cipher for authenticating. Also some PCD’s have secure models and key handling capabilities for secure communication between PCD and PICC for banking and transaction related applications.
There are many semiconductor companies who provide the RFID reader chips, with many enhanced features.NXP semiconductors and STMicroelectronics are world leaders in providing RFID reader chips. NXP semiconductors has a family of RFID/NFC chips with many enhanced features.
For more indepth knowledge on PCD, viewers can refer to:Radio-frequency identification – Wikipedia.
In the upcoming blog, we are going to interface NXP semiconductors MFRC522 and PN512 with host MCU. By making its device driver and to showcase the working of PCD’s
RFID Tag(PICC)
PICC (Proximity Integrated Circuit Card): These are the RFID Tags, which are known as Proximity Integrated Circuit cards, in technical terms. PICC are attached to the objects which need to be tracked. PICC consists of an antenna for generation of radio waves and memory for storing the UID and other information of PICC. Each PICC has a Unique value hardcoded inside them. This unique value is referred to as UID. The UID value is 7 bytes. PICC have memory divided in terms of blocks and sectors for storing the important information.
There are mainly 2 types of PICC/RFID tags. Active tags and Passive tags.
Active tags: They have on chip batteries; thus, they can operate at bigger distances and can operate at higher frequencies.
Passive tags: They don’t have an on-chip battery, instead they get energized and get the power from the PCD’s.magnetic fields. Thus, Passive tags need to be brought in very close proximity to PCD of about 1-2 cm, for decoding its value.
Also, tags are available in many different shapes, depending on the application. They come in credit card-based shapes, to small key ring-based shapes. Also, some tags have crypto features inside them for authentication purposes when PCD’s communicate with them. NXP semiconductor is a world leader in providing RFID Tag chips. Their MIFRAME family of RFID tags has been implemented in 1000’s of devices and use cases.
PCD and PICC communicate with each other according to ISO14443 spec. There are certain commands specified in that protocol, which are at first transmitted by PCD’s and then corresponding PICC responds, and the communication session is initialized.
For more in-depth knowledge on PICC, viewers can refer to:Radio-frequency identification – Wikipedia.
NXP semiconductor is a world leader in providing RFID Tag chips. Their MIFRAME family of RFID tags has been implemented in 1000’s of devices and use cases. There are many products in the MIFRAME family.One can refer to MIFARE (HF) | NXP Semiconductors, to know about these. We are going to use MIFRAME CLassic : MF1S503x, MF1S703x & MF1S703x RFID tags to make the driver for RFID reader MFRC522 in upcoming blog.
Applications of RFID
From agriculture to jewelry business, defense to kiosks, laundry automation to library system, RFID has various major real-world applications in different sectors. Here I would be listing some of the Applications of RFID technology:
- Highway Toll Collection and intelligent transportation system
- RFID card-based ignition system in Automotive: Theft rates for car models equipped with RFID starters, immobilizers and entry systems. In the 1990s, many a car thief was thwarted by the rather brilliant addition of RFID immobilizers to regular old physical keys. An RFID immobilizer is a chip embedded in the top part of an ignition key. This chip sends out an encrypted string of radio-frequency signals, basically a particular number of impulses broadcast on various radio frequencies to create a specific code, when the driver inserts it into the ignition-key slot. Without this code, the car either won’t start or won’t activate the fuel pump. So even if someone hotwires the car or copies an ignition key, the ignition isn’t going to work because it hasn’t received the proper radio-frequency code.
- RFID Technology in logistics and Supply Chain management: Supply chain management is one of the main areas where RFID has proven to be of great invention. With the beginning of production of products in factories, there is need to record the data such as expiration date, manufacture date, temperature, and more. So, RFID tags are attached with the products, each RFID tag has a unique code means each product can be distinguished via RFID tags. The needed data can be saved on these RFID tags. Further after factories, at the Warehouse/Distribution centers, these RFID tags can be read by RFID readers. This allows for instant reconciliation against inventory order lists.
The technology has evolved quite a bit since its first application many years ago. Now major brands and retailers like Walmart, Amazon, H&M, and Nike use RFID tags to track inventory and provide a better customer experience.
- RFID based attendance and entry system. In many corporate places and culture, there is use of RFID system for daily attendance and check-in time of the employes.RFID is being used actively in retail, healthcare, and other sectors to monitor workers. Since the workers in these sectors are large in number, hard to handle. Every employe is given a Card, which is in actual is RFID Tag. These tags store the information about the employe. Further RFID receivers are installed at different entry and exist location, which are connected to main computer/servers. On punching the employee card (which is basically a RFID Card), onto these RFID receivers the system gets the information saved on the card i.e is basically information about the employee.
What is difference between RFID & NFC?
The key difference between RFID and NFC,
Working principal of RFID technology?
To understand in simplest terms, in RFID there is wireless transfer of data from RFID tags and RFID receivers. RFID system is for small distances upto some meters and centimeters, not unlike Wi-Fi or BLE for long distances. So in the RFID system there is not much advanced or complicated RF front head & circuit. Instead, there is antenna which mainly do the wireless transfer via electric coupling with some modulation techniques. Coupling is the transfer of energy & data from one electronic circuit to another electronic circuit.
The core working principle of RFID is based on coupling via electromagnetic induction. If to go into the core physics/electronics of RFID: Electromagnetic Induction, Mutual Inductance, Modulation Techniques, Inductive coupling and Backscatter coupling are the things.
RFID tags consist of the antenna and the microchip. Microchip is the one which process,configures and stores the data. Antenna is used to communicate from RFID receivers.
RFID receivers consist of transceivers, microprocessors, communication interfaces and power supply.
Now what happens, as RFID receivers are powered up they start generating the magnetic field through its antenna. The intensity of this magnetic field is dependent on the frequency of RFID that we have chosen. Now as and when RFID tags are brought near to the RFID receivers, they get powered up through the magnetic field generated by receivers via coupling. This causes the nearby tag to couple with the reader and allows the stored data in the RFID tag to be read by the RFID receiver. Will not be going into much detail about thi. But to conclude the core working principle of RFID is coupling. There are 2 types of coupling mainly used: Inductive coupling and backscatter coupling.
RFID systems operating at 125–135 kHz and 13.56 MHz use inductive coupling, while those operating beyond 100 MHz, such as 860–960 MHz and 2400 and 5800 MHz use backscatter (radiative) coupling.
Now how should RFID tag and reader couple together & how data should be transferred, for that there is a standard defining the physical characteristics and working interaction b/w contactless tags and devices operating at 13.56 MHZ. ISO 14443 is an international standard governed by the ISO for RFID readers and tags.
What is ISO/IEC 14443?
ISO 14443 is an international standard governed by the ISO defining the physical characteristics and working interaction between contactless (proximity) tags and devices operating at 13.56 MHz (NFC – RFID) at up to 10 cm in distance.
ISO 14443 is the underpinning standard for many types of NFC tags and devices, although not often directly used by developers as the specific details are abstracted by other higher-level technology layers. Within 14443, a tag is referred to as a PICC (proximity integrated circuit card: Contactless Card) and a device as a PCD (proximity coupling device: Contactless Reader).
ISO/IEC 14443 Part1: Physical characteristics, specifies in which the physical dimensions of the card should be compliant with ISO/IEC 7810 or ISO/IEC 15457-1
ISO/IEC 14443 Part2: Radio frequency power and signal interface which specifies characteristics of the fields to be provided for power and bi-directional communication between proximity coupling devices (PCDs) and proximity cards or objects (PICCs).
ISO/IEC 14443 Part3: Initialization and anti-collision, which defines polling for proximity cards or objects (PICCs) entering the field of a proximity coupling device (PCD); the frames and timing used throughout the beginning phase of communication between PCDs and PICCs; the byte format etc.
ISO/IEC 14443 Part4: Transmission protocol which specifies transmission protocol including features like the special needs of contactless conditions and defines the activation and deactivation sequence of the protocol.
There are 2 types under ISO/IEC 14443 standard, type A & B both of which communicate via radio at 13.56 MHz’s . The main difference between these 2 types are:
→ Modulation Schemes, coding Schemes (Part2)
→ Protocol Initialization Procedures (Part3)
Transmission Protocol (Part4) is the same in both cases.
Projects associated with RFID
Author







