SPI Peripheral In STM32F103
Overview
So, in this blog we will be covering another alternate functionality of GPIO pins i.e SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface). Previously we hve covered following peripherals implementation in STM32F103 MCU’s.
- ADC(Analog To Digital Converter) in STM32F103
- UART Peripheral in STM32F103
- GPIO Peripheral in S32K144 MCU
- Clock Peripheral in STM32F103
- PWM on STM32F103
 SPI is a synchronous and full duplex communication between a master and several slave devices. It is used in devices or sensors in which speed is a priority . It operates at data transmission rate 8 Mbits or more. The protocol uses 3 or usually 4 wires for data transmission and receiver .It is used by various sensors and modules such as OLED Display, BMP280 , RC522 , DAC , Shift Registers etc.
SPI is a synchronous and full duplex communication between a master and several slave devices. It is used in devices or sensors in which speed is a priority . It operates at data transmission rate 8 Mbits or more. The protocol uses 3 or usually 4 wires for data transmission and receiver .It is used by various sensors and modules such as OLED Display, BMP280 , RC522 , DAC , Shift Registers etc.
SPI Theory
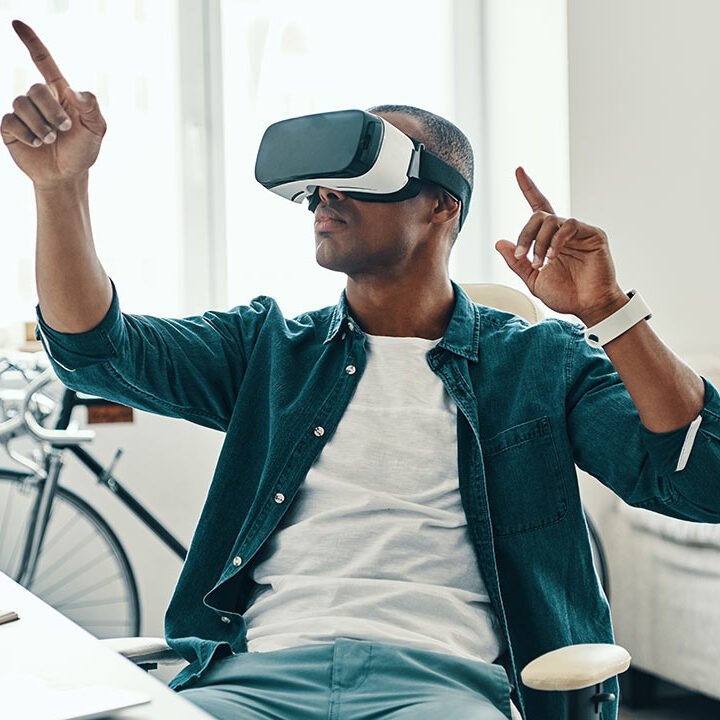
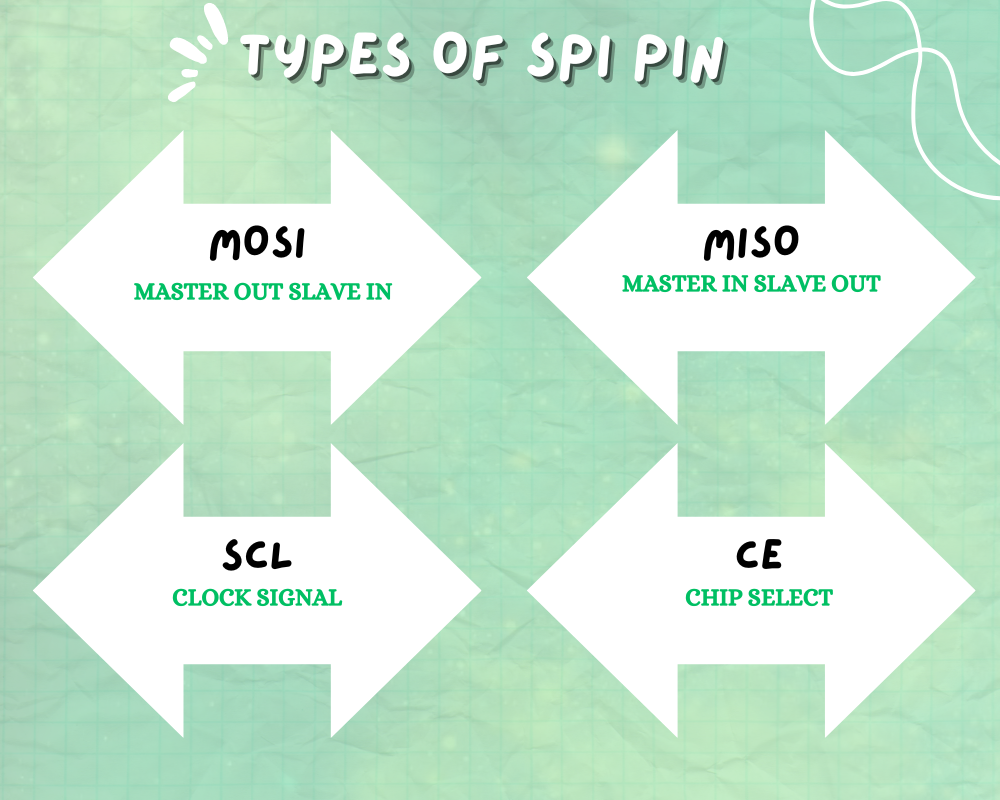 The SPI uses 2 pins for data transfer SDIN and SDO , SCLK clock for synchronization of data transfer between 2 chips, CE chip select that is used to initiate and terminate the data transfer.
The SPI uses 2 pins for data transfer SDIN and SDO , SCLK clock for synchronization of data transfer between 2 chips, CE chip select that is used to initiate and terminate the data transfer.
SDI = MOSI
SDO = MISO
SCLK = SCK
CE = SS
Besides SPI communication the SPI interface can switch between I2S communication protocol that is a synchronous serial communication interface. It supports 4 audio standards including the I2S Philips standard, the MSB- and LSB-justified standards, and the PCM standard. The operating modes can be full duplex(4 wires) and half duplex (6 wires)

Multi Mode Configuration
Multiple subnodes can be used with a single SPI main. The subnodes can be connected in regular mode or daisy-chain mode.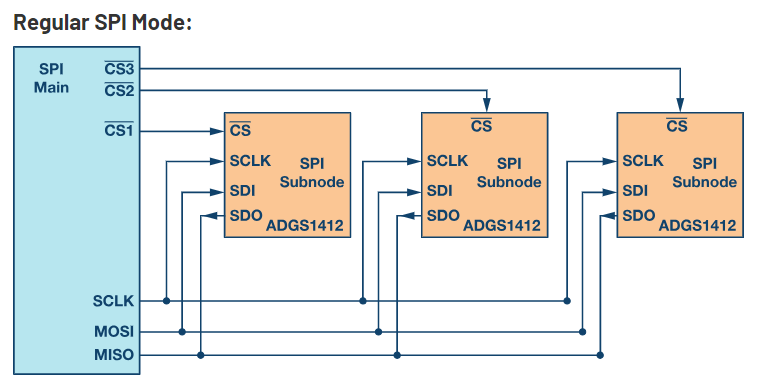
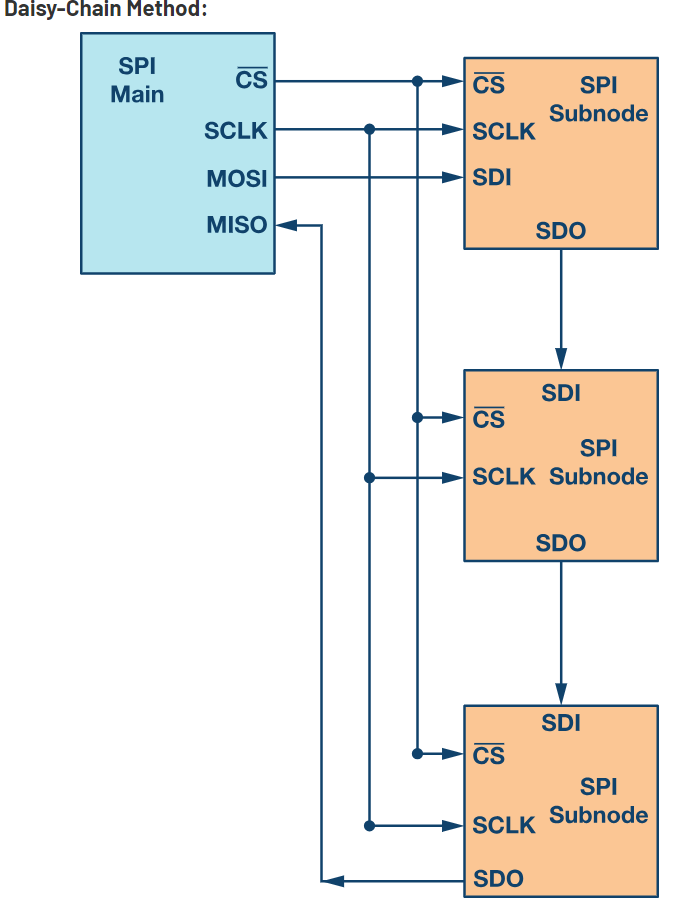
How Data is Transmitted in SPI
- Initially SCK is enabled that starts the transmission
- The master sets the SS line low of the slave
- Data is usually shifted out with most significant bit first , shifting a new least significant bit into the same register
- Data in slave side is shifted into least significant bit of the register
- Hence after all the shifting is done the master and slave has transferred the data
- If more data is to be exchanged the registers are reloaded and the process is repeated
- When no more data transmission is there the master stops toggling the SCK and deselects the slave using SS
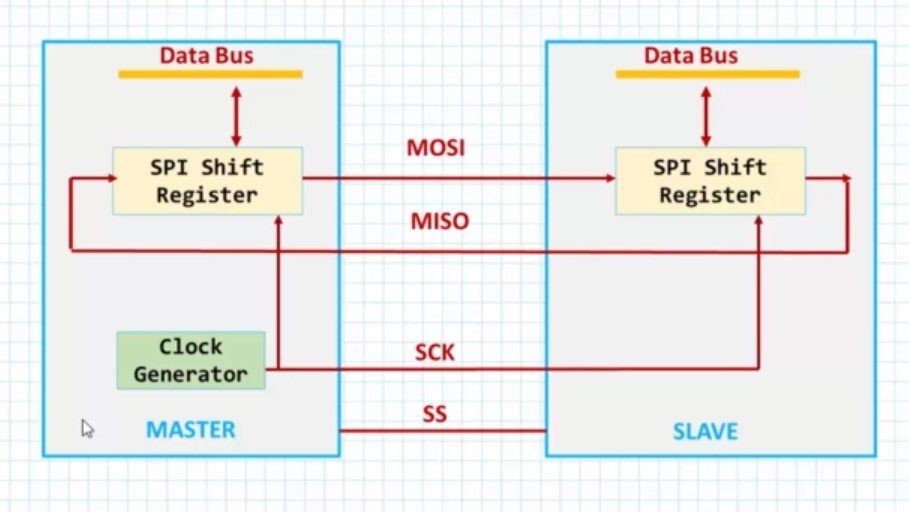
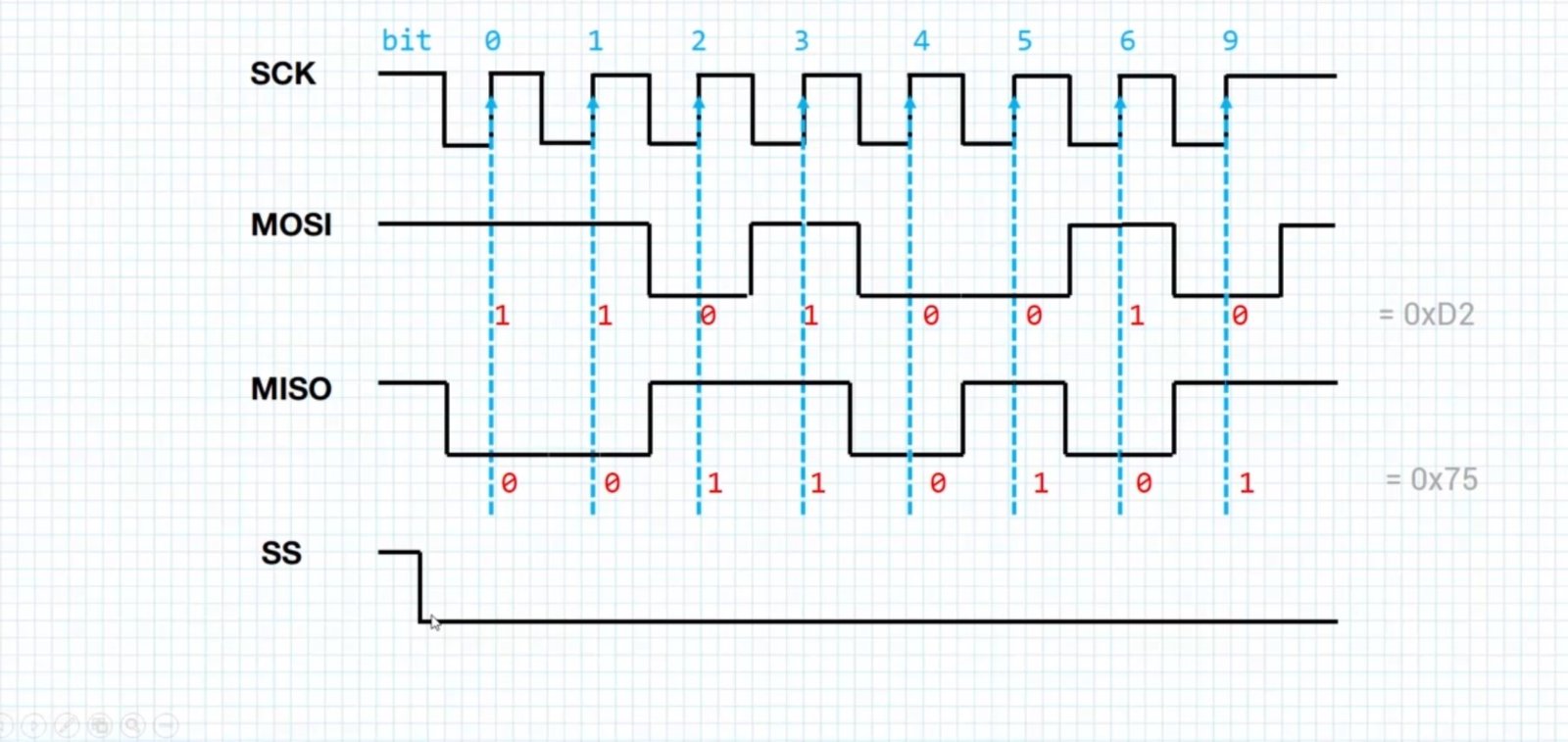
SPI Peripheral Bus Modes
Before discussing about the various bus modes we will be discussing the clock phase and polarity i.e CPOL:Clock Polarity and CPHA:Clock Phase and it is the combination of CPOL and CPHA that is referred to as Bus Modes.
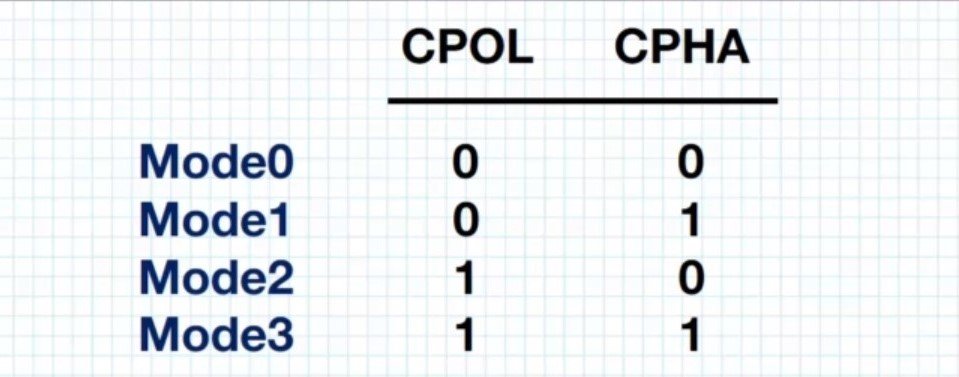
CPOL = 0
- Active state of clock = 1
- Idle state of clock= 0
- Means the sampling on the first edge
- CPHA = 0 – Data is captured on the rising edge and output on falling edge
- CPHA = 1 – Data is captured on the falling edge and output on the rising edge
CPOL = 1
- Active state of clock = 0
- Idle state of clock = 1
- Means sampling is on the second edge
- CPHA = 0 – Data is captured on the falling edge and output on rising edge
- CPHA = 1 – Data is captured on the rising edge and output on the falling edge
SPI Features in STM32F103
- Full-duplex synchronous transfers on three lines
- Simplex synchronous transfers on two lines with or without a bidirectional data line
- 8- or 16-bit transfer frame format selection
- Multimaster mode capability
- 8 master mode baud rate prescalers (fPCLK/2 max.)
- Slave mode frequency (fPCLK/2 max)
- Faster communication for both master and slave
- NSS management by hardware or software for both master and slave: dynamic change of master/slave operations
- Programmable clock polarity and phase
- Programmable data order with MSB-first or LSB-first shifting
- Dedicated transmission and reception flags with interrupt capability
- SPI bus busy status flag
-
Hardware CRC feature for reliable communication:
– CRC value can be transmitted as last byte in Tx mode
– Automatic CRC error checking for last received byte - Master mode fault, overrun and CRC error flags with interrupt capability
- 1-byte transmission and reception buffer with DMA capability: Tx and Rx requests
SPI Instances in STM32F103
SPI instances vary from microcontroller to microcontroller from 1 in stmf103c6t6a to 6 in stm32f7 each having different pins NSS pulse mode , TI mode and hardware crc calculations
SPI1 features PA5 as SCK , PA6 as MOSI and PA7 as MISO
SPI2 features PB3 as SCK, PB4 as MISO and PB5 as MOSI.
NSS Management in SPI protocol for STM32F103
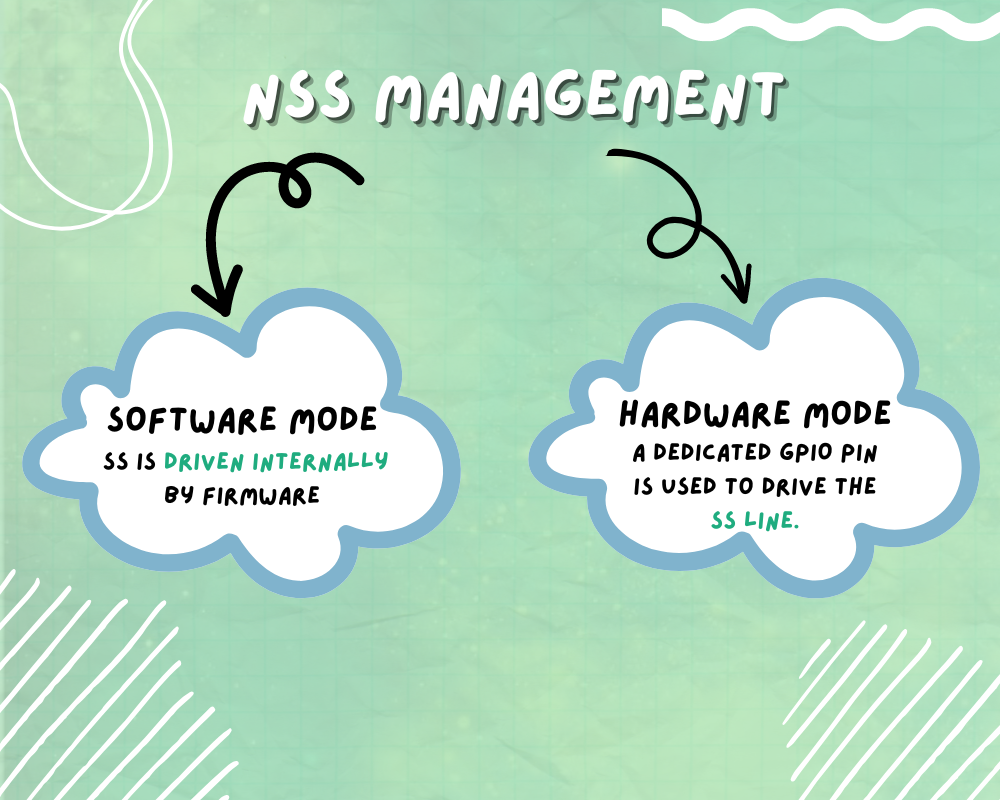 NSS line can to be driven via 2 modes
NSS line can to be driven via 2 modes
- Software Mode- SS is driven internally by firmware
- Hardware Mode – A dedicated GPIO pin is used to drive the SS line
Also NSS features NSS output and output disabled mode. Output mode is used only when device operates in master mode and it is disabled allowing mutli master capability
NSS hardware mode must be used in TI mode . CPHA and CPOL are forced to conform to Texas Instrument (TI) protocol requirements. In this NSS signal pulses at the end of every transmitted byte
APPLICATIONS OF SPI PROTOCOL




How to Configure SPI Peripheral for STM32F103
We would be using STM32 HAL and STM32CubeIDE for using the SPI peripheral in STM32F103 in this blog tutorial series.
CONFIGURATION IN STM32CUBEIDE

FIG 1- Selecting MOSI, MISO , SS and SCK pins
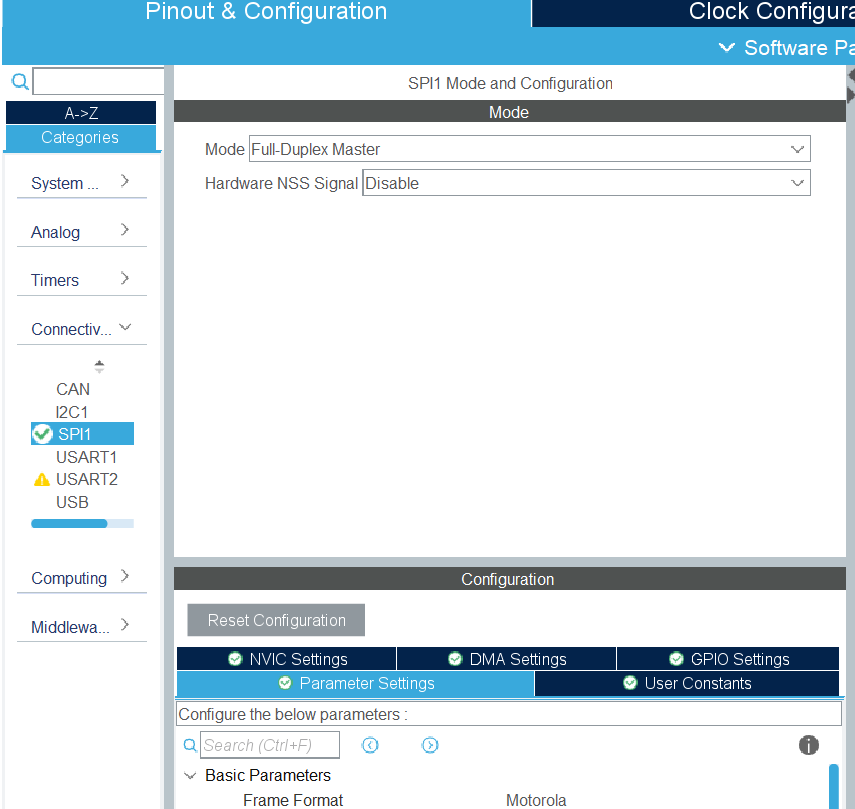 FIG2 – Selecting the operating mode
FIG2 – Selecting the operating mode
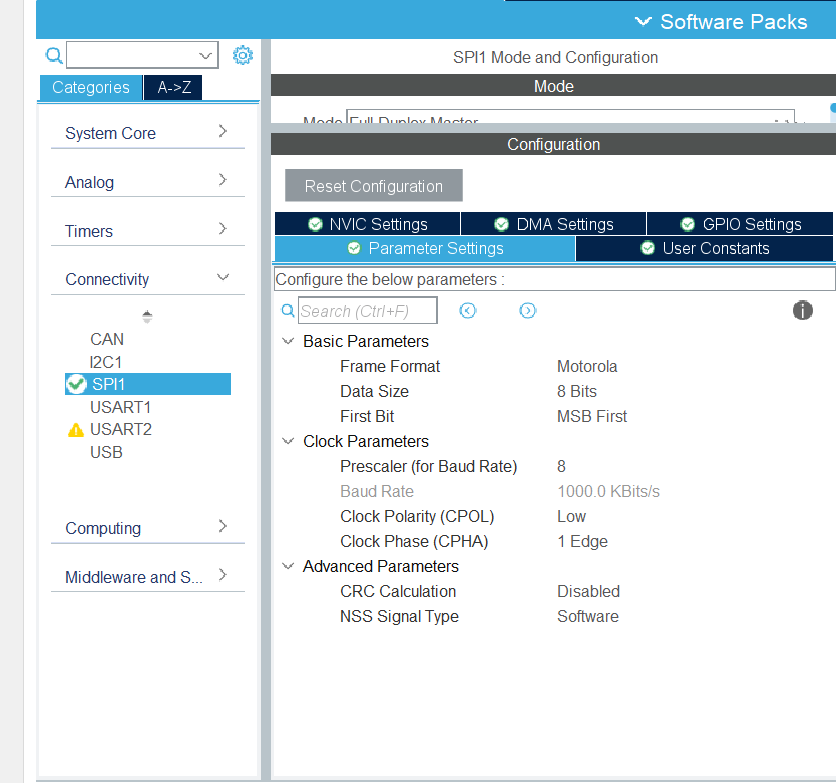
FIG3 – Configuring the parameters
- Intialize the GPIO inittypedef structure and enable the clock to both the port for which the alternating mapping is being used in our case that will be PORT A and also enable clock for the SPI peripheral
- Using Init API intialize the peripheral
- Configure the GPIO parameters such as
- Pins: This includes the pins that are being used for SPI
- Mode: This is used to expose the alternate functionality of the peripheral in which condition it is used push , pull or push pull.
- Alernate : Selects the alternate functionality of the register in our case it will be AF5
- Pull- Selects if the pin has to be pulled up or not
- Speed - Determines the speed of operation of the peripheral i.e low, medium, high or even very high in some cases
- Next we configure the SPI peripheral which in our case will be SPI1 but can be SPI2 in some cases too
- Mode:The mode of the device has to be set which can be either master or slave
- Direction:Specifies the bidirectional mode of SPI which can be Direction 2 lines , Direction 2 lines RX only, Direction 1 line only
- Datasize : The size of data that has to be send which can 8 bits or 16 bits
- CLKPolarity : This specifies the polarity of the clock which can be low or high
- CLKPhase : This parameter sets the clock phase which can be 1 edge or 2 edge
- NSS: This specifies the NSS is managed by software or hardware.The values can be software , hardware input or hardware output
- Baudrateprescaler : Specifies the amount by which the Baudrate is going to be divided by the values can range from 2 - 256 in the powers of 2
- FirstBit: This configures how the first bit will be transmission MSB first or LSB
- TIMode:This sets or unsets the TI Mode i.e if the TI Mode is enable or disabled
- CRCCalculation: This parameter specifies if the CRC or cyclic redundancy check is enabled or not
- CRCPolynomial : This is used for polynomial calculations which has to be odd number ranging from 1 to 65535.
SPI Data Handling API Types
In polling mode the CPU’s normal operation is stopped or blocked until the data is transmitted or received . The microcontroller has to be turned on for the whole operation
For eg – HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Transmit (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi, uint8_t * pData, uint16_t Size, uint32_t Timeout)
In interrupt mode the CPU fires an interrupt when data starts receiving and when the process is completed it notifies by firing an interrupt signal . CPU can continue its normal operation during this . In this mode the Interrupt priority is also set and IRQ is enabled . In the callback function the process occurs
For eg – HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Transmit_IT (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi, uint8_t * pData, uint16_t Size
The DMA mode is the most efficient way or data transmission in which the data is received in the preprogrammed memory location . Hence in this mode there is no intervention from the CPU and once the data transmission is done the CPU notifies
For eg – HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi, uint8_t * pData, uint16_t Size)
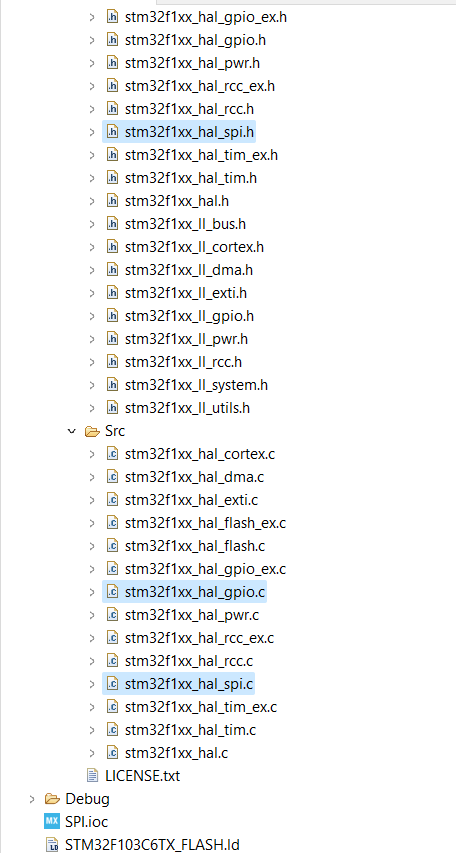
SDK Files
- Stm32f1xx_hal.c
- Stm32f1xx_hal_spi.c
- Stm32f1xx_hal_spi.h
The hal.c contains all the macros and function declaration of the GPIO pins the clock configuration and the alternate function mapping of the GPIO pins.The SPI.C function has the declaration and initialization of the SPI function including various parameters , static function and SPI INIT Function . The SPI function contains various macros that establish the various values the functions in SPI.c files functions can attain it includes structure parameters and enumerations.
HAL APIs Involved
- HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Init (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi)
- void HAL_SPI_MspInit (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi)
- HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Transmit (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi, uint8_t * pData, uint16_t Size, uint32_t Timeout)
- HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Receive (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi, uint8_t * pData, uint16_t Size, uint32_t Timeout)
- HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_TransmitReceive (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi, uint8_t * pTxData, uint8_t * pRxData, uint16_t Size, uint32_t Timeout
- static void MX_SPI1_Init(void)
FUNCTION NAME
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Init (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi)
FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
This function initializes the SPI peripheral according to the parameters and intialize the handle typedef
PARAMETERS
hspi: pointer to a SPI_HandleTypeDef structure that contains the configuration information for SPI module.
RETURN VALUES
HAL-STATUS
FOR EXAMPLE
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Init(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi)
{
/* Check the SPI handle allocation */
if (hspi == NULL)
{
return HAL_ERROR;
}
/* Check the parameters */
assert_param(IS_SPI_ALL_INSTANCE(hspi->Instance));
assert_param(IS_SPI_MODE(hspi->Init.Mode));
assert_param(IS_SPI_DIRECTION(hspi->Init.Direction));
assert_param(IS_SPI_DATASIZE(hspi->Init.DataSize));
assert_param(IS_SPI_NSS(hspi->Init.NSS));
assert_param(IS_SPI_BAUDRATE_PRESCALER(hspi->Init.BaudRatePrescaler));
assert_param(IS_SPI_FIRST_BIT(hspi->Init.FirstBit));
/* TI mode is not supported on this device.
TIMode parameter is mandatory equal to SPI_TIMODE_DISABLE */
assert_param(IS_SPI_TIMODE(hspi->Init.TIMode));
FUNCTION NAME
void HAL_SPI_MspInit (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi)
FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
This function initializes the Msp of SPI
PARAMETERS
hspi: pointer to a SPI_HandleTypeDef structure that contains the configuration information for SPI module.
RETURN VALUES
NONE
FUNCTION NAME
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Transmit (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi, uint8_t * pData, uint16_t Size, uint32_t Timeout)
FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
This function transmits certain amount of data in blocking mode
PARAMETERS
- hspi: pointer to a SPI_HandleTypeDef structure that contains the configuration information for SPI module.
- pData: pointer to data buffer
- Size: amount of data to be sent
- Timeout: Timeout duration
RETURN VALUES
HAL-STATUS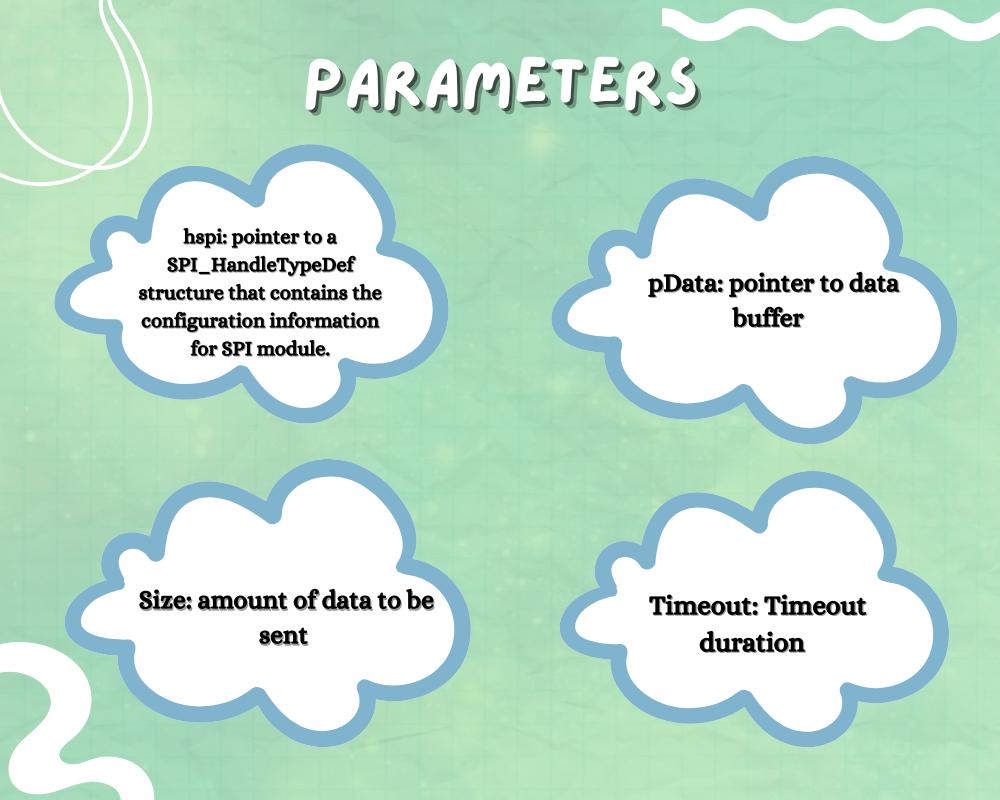
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_SPI1_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
/* USER CODE END 2 */
HAL_SPI_Transmit(&hspi1,tx_buffer,10,100);
FUNCTION NAME
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_TransmitReceive (SPI_HandleTypeDef * hspi, uint8_t * pData, uint16_t Size, uint32_t Timeout)
FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
This function is used to both transmit as well receive certain amount of data in blocking mode
PARAMETERS
- hspi: pointer to a SPI_HandleTypeDef structure that contains the configuration information for SPI module.
- pTxData: pointer to transmission data buffer
- pRxData: pointer to reception data buffer
- Size: amount of data to be sent and received
- Timeout: Timeout duration
RETURN VALUES
HAL-STATUS
HAL_SPI_TransmitReceive(&hspi1,tx_buffer,rx_buffer,10,100);
FUNCTION NAME
static void MX_SPI1_Init(void)
FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
This function is used to intialize the SPI1 along with the parameters
PARAMETERS
NONE
RETURN VALUES
NONE
static void MX_SPI1_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN SPI1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END SPI1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN SPI1_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END SPI1_Init 1 */
/* SPI1 parameter configuration*/
hspi1.Instance = SPI1;
hspi1.Init.Mode = SPI_MODE_MASTER;
hspi1.Init.Direction = SPI_DIRECTION_2LINES;
hspi1.Init.DataSize = SPI_DATASIZE_8BIT;
hspi1.Init.CLKPolarity = SPI_POLARITY_LOW;
hspi1.Init.CLKPhase = SPI_PHASE_1EDGE;
hspi1.Init.NSS = SPI_NSS_SOFT;
hspi1.Init.BaudRatePrescaler = SPI_BAUDRATEPRESCALER_8;
hspi1.Init.FirstBit = SPI_FIRSTBIT_MSB;
hspi1.Init.TIMode = SPI_TIMODE_DISABLE;
hspi1.Init.CRCCalculation = SPI_CRCCALCULATION_DISABLE;
hspi1.Init.CRCPolynomial = 10;
CODE
EXERCISE- Transmit data in TX buffer and receive it in the RX buffer
#include "main.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
/* USER CODE END PTD */
/* Private define ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private macro -------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PM */
/* USER CODE END PM */
/* Private variables ---------------------------------------------------------*/
SPI_HandleTypeDef hspi1;
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private function prototypes -----------------------------------------------*/
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
static void MX_SPI1_Init(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
/* USER CODE END PFP */
/* Private user code ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
/* USER CODE END 0 */
uint8_t tx_buffer[10]= {10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100};
uint8_t rx_buffer[10];
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_SPI1_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
/* USER CODE END 2 */
HAL_SPI_TransmitReceive(&hspi1,tx_buffer,rx_buffer,10,100);
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}
/**
* @brief System Clock Configuration
* @retval None
*/
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
/** Initializes the RCC Oscillators according to the specified parameters
* in the RCC_OscInitTypeDef structure.
*/
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSI;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSIState = RCC_HSI_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSICalibrationValue = RCC_HSICALIBRATION_DEFAULT;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_NONE;
if (HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB buses clocks
*/
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK
|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_HSI;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV1;
if (HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_0) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
/**
* @brief SPI1 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_SPI1_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN SPI1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END SPI1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN SPI1_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END SPI1_Init 1 */
/* SPI1 parameter configuration*/
hspi1.Instance = SPI1;
hspi1.Init.Mode = SPI_MODE_MASTER;
hspi1.Init.Direction = SPI_DIRECTION_2LINES;
hspi1.Init.DataSize = SPI_DATASIZE_8BIT;
hspi1.Init.CLKPolarity = SPI_POLARITY_LOW;
hspi1.Init.CLKPhase = SPI_PHASE_1EDGE;
hspi1.Init.NSS = SPI_NSS_SOFT;
hspi1.Init.BaudRatePrescaler = SPI_BAUDRATEPRESCALER_8;
hspi1.Init.FirstBit = SPI_FIRSTBIT_MSB;
hspi1.Init.TIMode = SPI_TIMODE_DISABLE;
hspi1.Init.CRCCalculation = SPI_CRCCALCULATION_DISABLE;
hspi1.Init.CRCPolynomial = 10;
if (HAL_SPI_Init(&hspi1) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN SPI1_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END SPI1_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief GPIO Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
/* USER CODE BEGIN MX_GPIO_Init_1 */
/* USER CODE END MX_GPIO_Init_1 */
/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */
__HAL_RCC_GPIOD_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();
/*Configure GPIO pin Output Level */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(SPI_CS_GPIO_Port, SPI_CS_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET);
/*Configure GPIO pin : SPI_CS_Pin */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = SPI_CS_Pin;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_HIGH;
HAL_GPIO_Init(SPI_CS_GPIO_Port, &GPIO_InitStruct);
/* USER CODE BEGIN MX_GPIO_Init_2 */
/* USER CODE END MX_GPIO_Init_2 */
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
/* USER CODE END 4 */
/**
* @brief This function is executed in case of error occurrence.
* @retval None
*/
void Error_Handler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Error_Handler_Debug */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the HAL error return state */
__disable_irq();
while (1)
{
}
/* USER CODE END Error_Handler_Debug */
}
#ifdef USE_FULL_ASSERT
/**
* @brief Reports the name of the source file and the source line number
* where the assert_param error has occurred.
* @param file: pointer to the source file name
* @param line: assert_param error line source number
* @retval None
*/
void assert_failed(uint8_t *file, uint32_t line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 6 */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the file name and line number,
ex: printf("Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %d\r\n", file, line) */
/* USER CODE END 6 */
}
#endif /* USE_FULL_ASSERT */
Author







